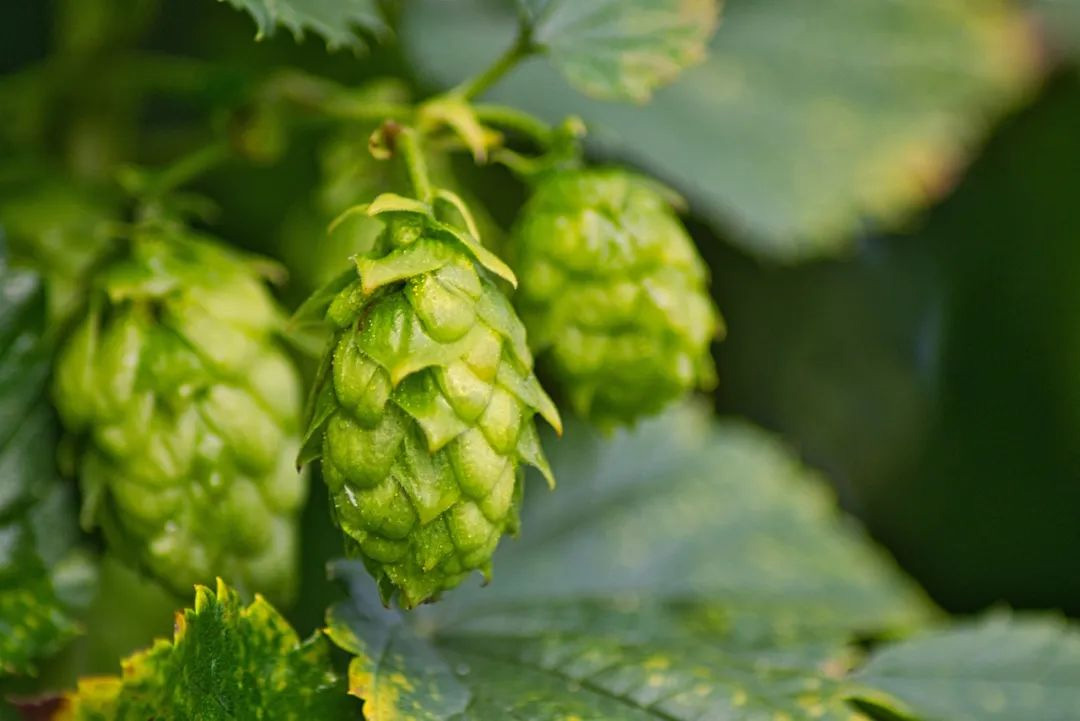
Under the churning foam of the amber beer lies an underestimated plant treasure. As early as the 9th century AD, it was used as a natural preservative by European brewers. Nowadays, it has become an indispensable raw material in beer brewing with its unique bitterness and aroma. This kind of plant is hops.
1. Hops: The magic weapon for brewing beer
Hop (Humulus lupulus), also known as snake hop, is a perennial climbing plant of the Cannabaceae family and can grow to more than 7 meters. It has dense conical inflorescences, which are botanically called cones and are composed of soft, light green resin petals. When mature, the cones of hops are covered with anthocyanin glands that secrete resin and essential oils, creating the unique flavor and aroma of the hop variety. Hop cones are usually picked at the end of August or in September.

Hops have been used as a medicinal herb since ancient Egyptian times. In Roman times, hops were used to improve liver diseases and digestive system disorders. Since the 13th century, hops have been regarded as a good medicine for improving fever and spleen diseases in the Arab region.
The use of hops in beer can be traced back to Europe in the 9th century AD. Initially, they were added to beer due to their preservative properties to extend the shelf life. During the Middle Ages, brewers in German monasteries discovered that it could balance the sweetness of malt, endow beer with a refreshing bitterness and a rich aroma, and thus established its core position in beer brewing. Today, approximately 98% of cultivated hops are mainly used in the beer brewing industry, and the United States is the world’s largest producer of hops.

2. Not only in brewing, hops have many more beneficial effects
Hops, with their unique bitterness and aroma, have become indispensable raw materials in beer brewing. However, its value goes far beyond this.
Modern research has found that hops contain α -acids (mainly humulone) and β -acids (mainly humulone), flavonols (quercetin and kaempferol), flavonoid 3-oils (mainly catechins, epicatechins and proanthocyanidins), phenolic acids (ferulic acid), and a relatively small amount of isoprene flavonoids (fulvic acid). Among them, alpha acids and beta acids are the main sources of the bitterness of hops.
Sedation and sleep aid: Humulone in hops can bind to GABA receptors, alleviating anxiety and promoting sleep. The GABA in hops can increase the activity of the neurotransmitter GABA, thereby inhibiting the central nervous system. An animal model experiment shows that a 2-milligram concentration of hop extract can effectively reduce nocturnal activity in the circadian rhythm. In conclusion, the sedative effect of hops is mediated by the enhanced function of GABA receptors, which are responsible for the rapid inhibitory synaptic transmission in the brain. At present, people often combine hops with valerian to make calming tea.
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects: Hops contain biomolecules with high antioxidant potential such as flavonols, rutin (quercetin-3-rutin glycoside), and astragaloside (kanophenol-3-glucoside), which can effectively prevent damage from reactive oxygen species. In addition, xanthol in hops can eliminate free radicals, inhibit the NF-κB pathway, and alleviate chronic inflammation (such as arthritis).
Antibacterial: Since ancient Egypt, hops have been used to preserve food. The bitter α -acid and β -acid in hops have antibacterial activity and can inhibit the growth of various microorganisms, including Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus epidermococcus, Streptococcus mutans and Gram-positive bacteria. This is also one of the reasons why beer has historically been safer than drinking water. In addition to endowing it with antibacterial properties, alpha-acid also helps maintain the foam stability of beer.
Supporting women’s health: Hop isoprenylnaringin (derived from fulminol and its derivatives) can compensate for the decrease in 17-β -estradiol levels during menopause. Hop preparations contain 8-isoprenylnaringin, which is one of the potent phytoestrogens known in the plant kingdom. Hop preparations can be used as a natural substitute for phytoestrogens during menopause in women to relieve hot flashes, insomnia and mood swings. A study involving 63 women showed that the use of hop preparations could alleviate menopause-related vasomotor symptoms and hot flashes.
Protecting nerves: Research has found that hop terpenes can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, protect nerves, provide anti-inflammatory protection for the brain, and reduce oxidative stress. Another study found that hop isoalphaic acid can enhance hippocampal dependent memory and prefrontal cortex related cognitive functions by activating dopamine neural transmission. The bitter acid in hops can enhance memory function through the mechanism mediated by norepinephrine neurotransmission. Hop isoalphaic acid can alleviate neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in various rodent neurodegenerative disease models, including Alzheimer’s disease.
3. The application of hops
Mordor data shows that the hop market size is estimated to be 9.18 billion US dollars in 2025 and is expected to reach 12.69 billion US dollars by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 6.70% during the forecast period (2025-2030). Driven by the growth in beer consumption, the trend of craft beer and the development of new hop varieties, the hop market is expected to continue to grow.
Justgood Health
A hop vegetarian capsule has been launched. This product has a sedative effect and helps with sleep.
Post time: Jun-24-2025



